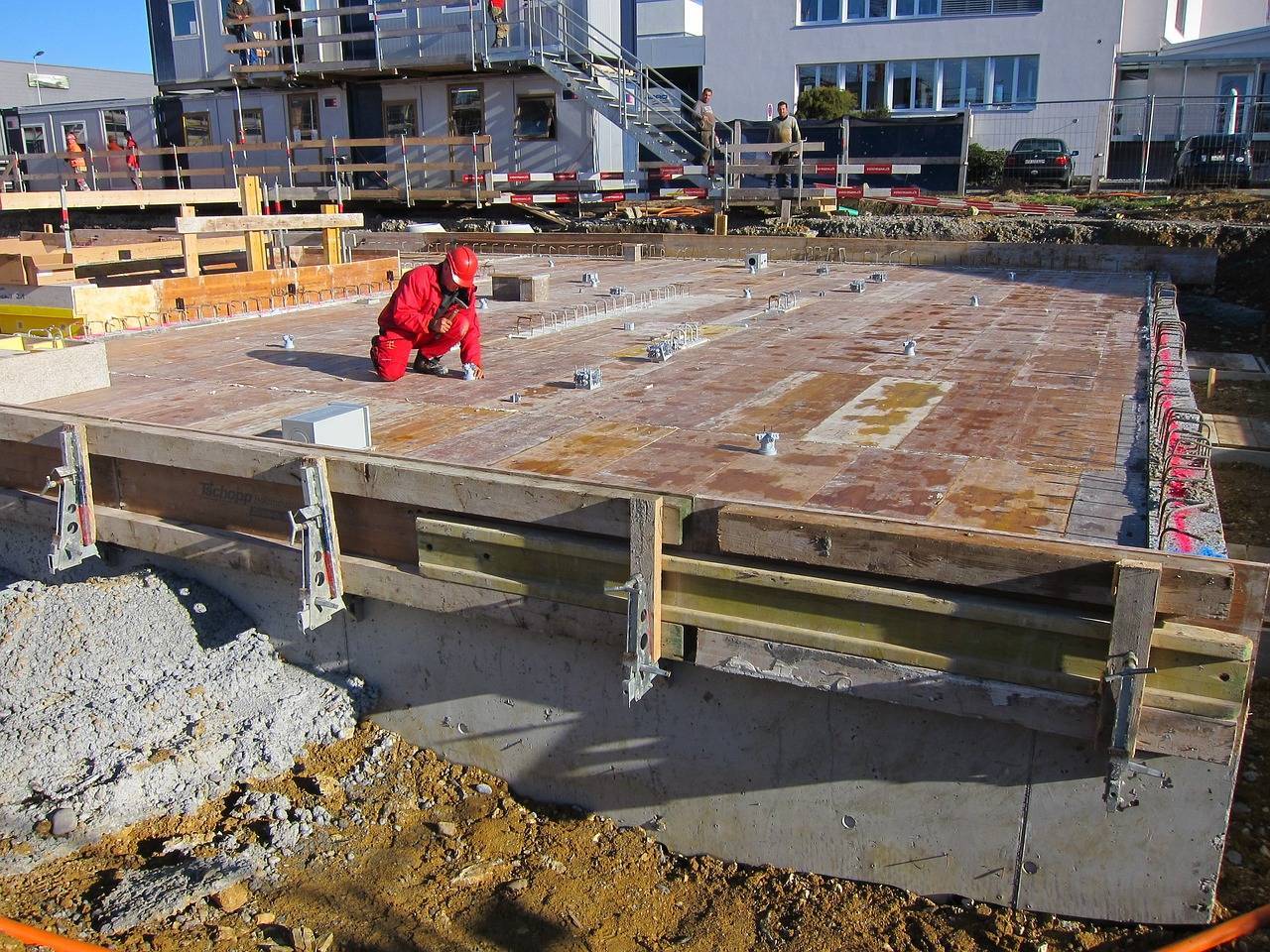
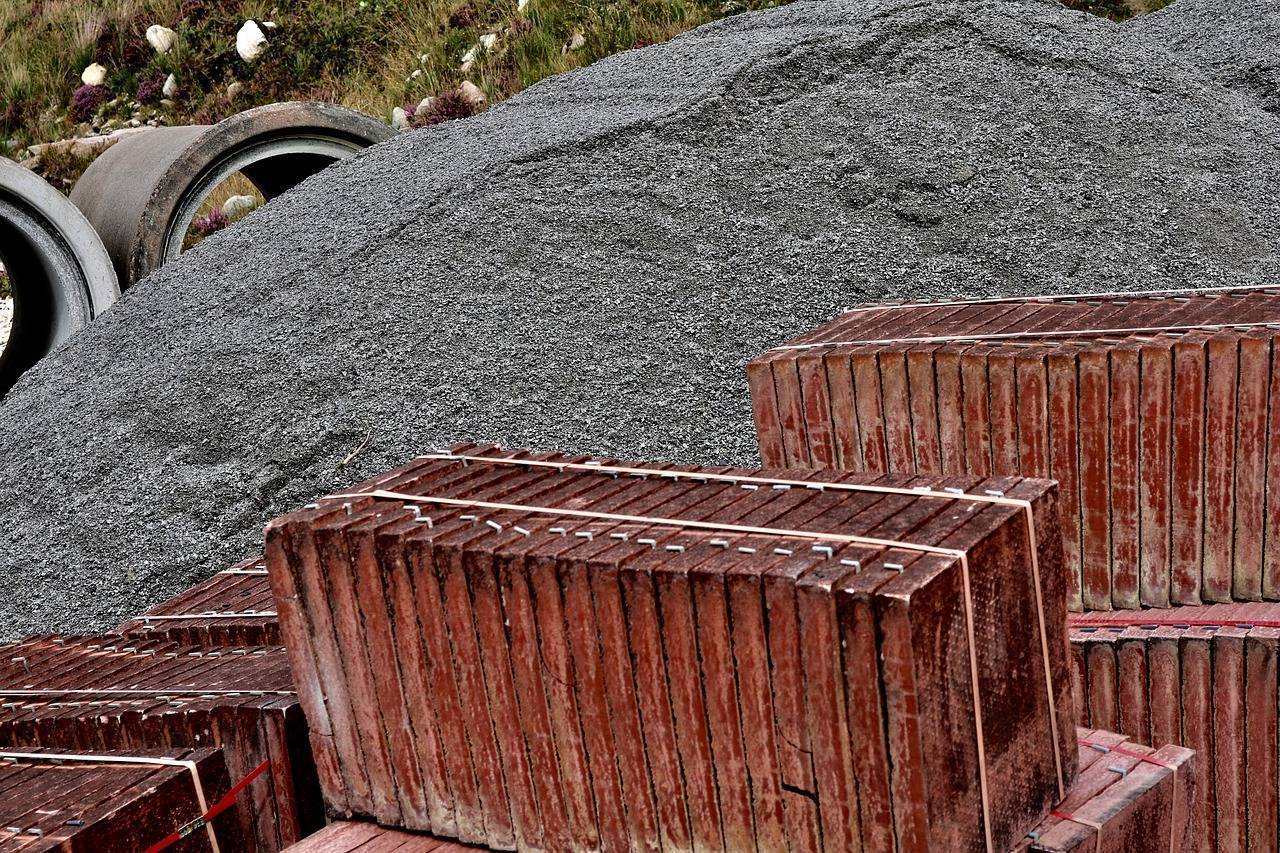
As the clamour for swift urbanization grows louder in India, the need for construction processes to be not just swift but cost-effective becomes increasingly paramount. To address these demands formwork emerges as an important solution, adept at meeting the evolving needs of construction projects with precision and efficiency. Acting as a temporary mold or structure, formwork plays an integral role in shaping and supporting wet concrete until it attains the requisite strength.The adaptable and versatile nature of formwork systems allows them to harmonise with a spectrum of architectural designs, catering to the diverse tastes prevalent in India's real estate market.
What is formwork and its importance?
Formwork refers to the temporary mold or structure used in construction to support and shape concrete until it sets and gains enough strength to support itself. It is an essential component in the construction process, ensuring that the concrete takes the desired shape and structure. Formwork can be made from various materials, including wood, steel, aluminum, or plastic, and it is designed based on the specific requirements of the construction project. Once the concrete has hardened and gained sufficient strength, the formwork is removed, leaving behind the finished structure.
Amidst the surging demand in India's real estate sector, the role of formwork systems becomes increasingly vital in meeting the industry's multifaceted needs. These systems offer a dynamic solution by expediting construction processes, addressing the urgency of timely project delivery. The inherent cost-effectiveness aligns seamlessly with the economic considerations of a market marked by high demand, enabling developers to navigate challenges while maintaining competitive pricing. Precision and versatility, characteristic of formwork systems, ensure the delivery of high-quality structures, meeting the discerning expectations of homebuyers and investors alike. In essence, formwork systems play a central role in navigating and fulfilling the dynamic requirements of India's rapidly expanding real estate sector.

How does it work?
Formwork is utlised providing a temporary mold or structure that supports and shapes wet concrete until it solidifies and gains the necessary strength. The process typically involves the following steps:
1. Design and Planning: Engineers design the formwork based on the architectural and structural requirements of the construction project. This includes determining the type of formwork system needed and its configuration.
2. Installation: The formwork is assembled on-site according to the design specifications. This involves placing panels, beams, or other formwork elements in the desired positions to create the shape of the concrete structure.
3. Reinforcement Placement: If needed, steel reinforcement is placed within the formwork to provide additional strength to the concrete structure.
4. Concrete Pouring: Once the formwork is in place and secured, concrete is poured into the mold. The formwork contains the concrete, giving it the desired shape.
5. Curing: After the concrete is poured, it undergoes a curing process to ensure proper hydration and strength development. The formwork system must remain in place during this period.
6. Stripping: Once the concrete has sufficiently cured and gained strength, the formwork is removed. This reveals the final structure, and the formwork components can be reused for subsequent pours if they are reusable systems.
Formwork systems can vary, including traditional timber formwork, steel formwork, and modern reusable systems made of plastic or aluminum. The choice of formwork system depends on factors such as the type of construction, project requirements, and the desired efficiency of the construction process.
Advantages of formwork
The use of formwork in construction offers several advantages:
1. Precision and Accuracy: Formwork allows for precise shaping of concrete structures, ensuring that the final product adheres to design specifications and architectural requirements.
2. Versatility: Formwork systems are adaptable to various shapes and sizes, accommodating the diverse architectural designs prevalent in construction projects.
3. Efficiency and Speed: Formwork, especially modern reusable systems, accelerates construction timelines by providing a quick and efficient means of molding and shaping concrete.
4. Cost-effectiveness: Formwork can contribute to cost savings by optimizing material usage, reducing labor requirements, and shortening construction schedules.
5. Structural Integrity: Formwork ensures that concrete structures attain the necessary strength and durability, meeting stringent safety and quality standards.
6. Sustainability: Reusable formwork systems minimize material wastage, aligning with sustainable construction practices and reducing the environmental impact of construction projects.
7. Safety: Properly designed and installed formwork enhances on-site safety by providing stable support for wet concrete and preventing structural failures during the construction process.
8. Consistency: Formwork helps maintain consistency in the appearance and dimensions of concrete elements, resulting in a uniform and aesthetically pleasing finished product.
Types of formwork
1. Timber Formwork: Traditional and cost-effective, timber formwork involves using plywood or wooden boards to create molds for concrete structures. While versatile, it may not be as durable as other materials.
2. Steel Formwork: This type involves using steel sheets, angles, and other components to create robust and reusable molds. Steel formwork is durable, provides a smooth finish, and is suitable for large and complex structures.
3. Aluminum Formwork: Similar to steel formwork but lighter, aluminum formwork is known for its durability, ease of handling, and the ability to be reused multiple times. It is often used for residential and commercial construction.
4. Plastic Formwork: Made from lightweight and durable plastic materials, this formwork is easy to handle and suitable for projects with repetitive structures. Plastic formwork is often used for small to medium-sized construction projects.
5. Fabric Formwork: This innovative approach involves using flexible and permeable fabric molds to shape concrete. It is particularly useful for creating curved or irregular shapes and is considered more environmentally friendly.
6. Engineered Formwork Systems: These are modular systems that can be customized to fit various construction needs. They often include components like prefabricated panels, props, and connectors, providing flexibility and efficiency.
7. Stay-In-Place Formwork: This type remains in place after the concrete sets, becoming a permanent part of the structure. Examples include insulated concrete forms (ICFs) and certain types of precast concrete elements.
8. Climbing Formwork: Designed for vertical structures like towers and high-rise buildings, climbing formwork is a self-supporting system that can be repositioned as the concrete structure advances vertically.
9. Slipformwork: Similar to climbing formwork, slipformwork is a continuous, non-stop method used for tall structures like towers and chimneys. It involves a moving formwork system that allows for a continuous pour and vertical construction.
10. Jump Formwork: This is a specialized type of climbing formwork used for the construction of vertical structures, especially tall buildings. The formwork is elevated in small sections, allowing for continuous upward construction.
11. Ganged Formwork: In this system, multiple interconnected forms are used simultaneously, speeding up the construction process for large, repetitive structures like walls and columns.
12. Table Formwork: Suited for floor slabs in building construction, table formwork consists of pre-assembled tables that can be lifted and repositioned, providing efficiency in creating large horizontal concrete surfaces.
13. Flexible Formwork: Made from materials like rubber or fiberglass, flexible formwork is used for creating curved or unique shapes in concrete construction, offering design flexibility and versatility.
14. Plywood Formwork: Plywood is commonly used in conjunction with other formwork systems. It is cost-effective, and its smooth surface produces a clean finish on the concrete
The choice of formwork depends on factors such as project complexity, budget, timeline, and the desired finish of the concrete structure. Different types of formwork offer distinct advantages and are selected based on the specific requirements of each construction project.
Prerequisites for selecting the formwork
Choosing the appropriate formwork for a construction project involves considering several prerequisites to ensure efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness. Here are key factors to consider:
1. Type of Structure: The nature of the structure being built significantly influences formwork selection. Different structures, such as residential buildings, bridges, or high-rise towers, may require specific formwork systems tailored to their unique shapes and dimensions.
2. Material Requirements: Consider the type of materials being used, especially the concrete mix. Some formwork systems may be better suited for specific concrete compositions or curing conditions.
3. Project Complexity: The complexity of the project, including architectural intricacies and structural design, influences the choice of formwork. Certain systems may be more adaptable to intricate designs or variations in construction.
4. Budget Constraints: Formwork costs can vary significantly, and budget constraints play a crucial role in the selection process. Balancing the need for quality formwork with cost considerations is essential for overall project affordability.
5. Construction Timeline: The construction schedule is a critical factor. Some formwork systems are designed for rapid assembly and disassembly, contributing to faster construction timelines. This is especially important in projects with tight deadlines.
6. Reusability: Consider the potential for reusing formwork components. Systems that allow multiple uses can result in cost savings over time, especially for contractors engaged in multiple projects.
7. Safety Requirements: Safety is paramount in construction. Formwork systems must adhere to safety standards and regulations. Factors such as load-bearing capacity, stability, and ease of handling contribute to a safe construction environment.
8. Environmental Impact: Increasing emphasis on sustainable construction practices necessitates considering the environmental impact of formwork materials and their disposal. Reusable formwork systems and those made from eco-friendly materials align with sustainable construction principles.
9. Availability and Lead Time: Ensure that the chosen formwork system is readily available and can be delivered within the project's timeline. Delays in obtaining formwork can impact the overall construction schedule.
10. Expertise and Training: Assess the expertise and training required for assembling and using the chosen formwork system. Availability of skilled labor familiar with the selected system contributes to efficient construction processes.
11. Local Regulations: Adherence to local building codes and regulations is crucial. Some areas may have specific requirements or restrictions regarding the use of certain formwork systems, and compliance is essential for project approval.
By carefully evaluating these prerequisites, construction professionals can make informed decisions when selecting the right formwork for a project, ensuring that it aligns with the specific needs and constraints of the construction endeavor.
Applications of formwork
1. Residential Construction: Formwork is extensively used in the construction of residential buildings, including single-family homes, multi-story apartments, and condominiums. It facilitates the creation of various structural elements like slabs, columns, and walls.
2.Residential Foundations: Formwork is used extensively in creating foundations for residential structures, including basement walls and footings. The stability and precision of formwork are critical in ensuring a strong and durable foundation.
3. Commercial Construction: In the commercial real estate sector, formwork is applied for constructing office buildings, retail spaces, and other commercial structures. Its versatility allows for the development of diverse architectural designs and layouts.
4. Industrial Facilities: Formwork is employed in the construction of industrial buildings and facilities. This includes manufacturing plants, warehouses, and distribution centers where robust and efficient construction is essential.
5. High-Rise Buildings: The construction of high-rise structures, such as skyscrapers and tall residential towers, relies heavily on formwork. Systems that support vertical construction and climbing formwork are often applied in these projects.
6. Educational and Institutional Buildings: Formwork is used in the construction of schools, universities, hospitals, and other institutional structures. It allows for the creation of various concrete elements required for these facilities.
7. Renovation and Retrofitting: Formwork is not limited to new construction; it is also used in renovation and retrofitting projects. It helps in replacing or enhancing existing concrete structures with updated designs and materials.
8. Custom Architectural Designs: Formwork is crucial for realizing custom and intricate architectural designs. It enables the construction of unique shapes, curves, and other design elements that contribute to the aesthetic appeal of a real estate project.
9. Energy-Efficient Construction: In the context of energy-efficient construction, formwork is applied in projects using insulated concrete forms (ICFs). These forms stay in place after the concrete sets, providing continuous insulation for the building.
The market potential of formwork in India; Driving Factors leading to demand
As per reportsanddata report, the global formwork market size was USD 5.32 Billion in 2018 and is projected to reach USD 6.37 Billion by 2027, at a CAGR of 2.29% from 2017 to 2027.
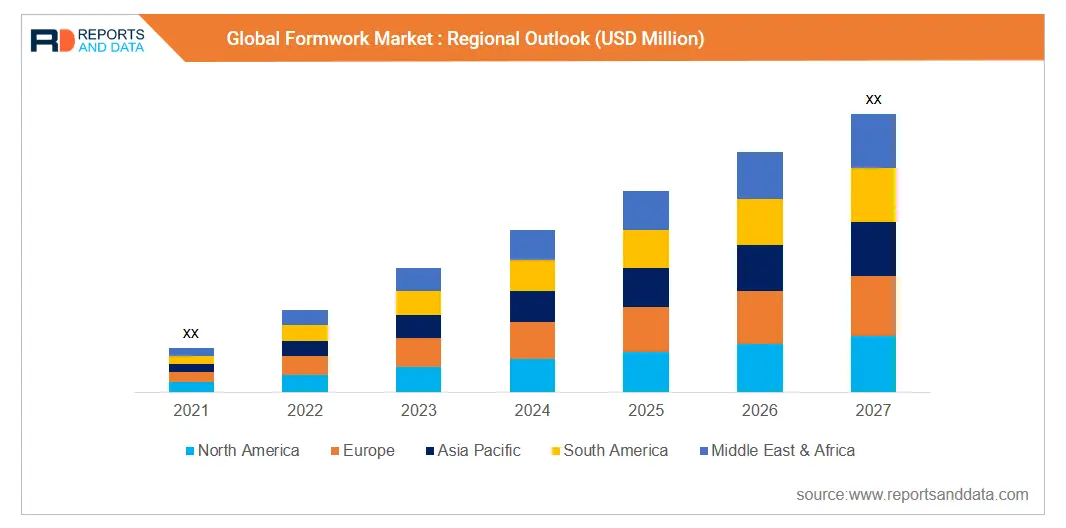
As per 6wresearch report, India formwork market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.8% during 2020-2026.
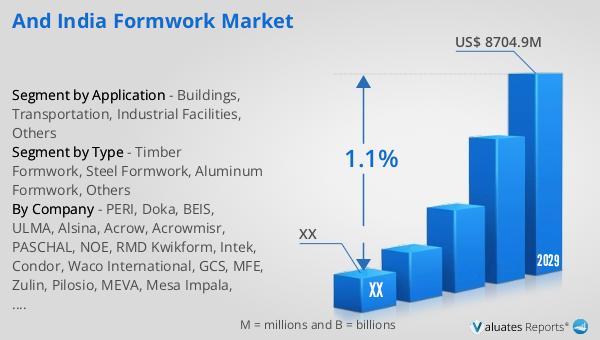
As per valuates report, the Formwork revenue in India Is expected to grow from US$ million in 2022 to US$ million by 2029, at a CAGR of % during the forecast period (2023-2029).
Growth driver for formwork in India
The major drivers for the growth are rising investments in infrastructure development, growing demand for residential real estate and construction activities across various sectors such as commercial, industrial and institutional projects. Increasing urbanization especially in tier I cities has resulted in huge investments from government as well as private players for infrastructure development across India which will further drive the market growth over the forecast years. Moreover, an increasing number of smart city projects will also contribute towards the growth of the Indian formwork industry over the coming years.
Government initiatives such as Smart City Mission (SCM) with an investment of USD 1 trillion along with Housing For All mission that aims to provide affordable housing to everyone by 2022 have provided ample opportunities for companies operating in this segment leading them to boost their revenues significantly over the past few years. Furthermore, favourable FDI regulations coupled with introduction of GST have eased out many difficulties faced by manufacturers while dealing in international markets thereby aiding them expand their business more efficiently all around the world which is expected to reflect positively on overall market size in coming years.
Conclusion
Formwork is indispensable in the realm of construction, weaving itself seamlessly into the intricate tapestry of real estate development. From the foundational elements of residential structures to the soaring heights of skyscrapers, formwork's adaptability and precision have become the backbone of modern construction practices. Its applications extend beyond mere structural support, influencing the very aesthetics and efficiency of buildings. As the construction industry continues to evolve, the advancements in formwork systems exemplify a commitment to enhancing both the speed and sustainability of building processes, ultimately shaping the skylines and communities of the future. In the intricate dance between form and function, formwork takes center stage, ensuring that the concrete structures we rely on are not just robust but also visually striking and environmentally conscientious.









